Overview and Key features of Blockchain technology
Blockchain Technology is a distributed Ledger that involves blocks as data stored in the form of networks and nodes is known to be a blockchain. Moreover, each block represents with a list of transactions and a record of actions. And every block represents a recorded transaction. The linkage represent in the form of chains. In blockchain decentralization, there is redundancy in the data distribution. If there is an altering of one record then the next record blocks it from preventing it with comparison of hashes and there is no alteration taking place. The work happens with encrypted proof of work and this includes irreversible transactions and legal contracts with the help of blockchain hashing algorithm (Hayes, 2024).
In immutability, there is no alteration of data, and various cryptographic techniques are used for linking the data from the previous one and record in the blockchain. Moreover, it helps to maintain fraud detection and integration of data. There are types of blockchains such as public blockchain in which it is accessible to everyone and everyone participates in the transactions. These are used in open industries. A private blockchain is the involvement of a small group of entities and authorized participants in making the transactions (Paul, Aithal, Saavedra, & Ghosh, 2021).The confidential information will be tracked and maintained in small organizations. Consortium blockchain is known as a semi-permissible blockchain where both the public and private blockchain are involved.
Blockchain Technology

Introduction to supply chain management and blockchain
Generally, supply chain management is a process of involvement in the production and distribution of goods and services. It is an important part of business operations where it involves management of goods in market shares and competitiveness. Moreover, It has made a great transformation with the involvement of consumers, suppliers, retailers, and distributors. Especially, the Supply chain has become an important aspect for innovative improvement in entire product distribution. It is a modern technology in supply chains as a digital Ledger and distributed network. Also, It contains a block of transactions and the blocks linked with the supply chain and proof of the system.
The single entity controls blockchain’s decentralized nature and makes sure to reduce transactions and transparency and maintain security (Tripathi, Ahad, & Casalina, 2023). Accordingly, Real-time Ledger and visibility of the flow of goods and services help in managing the product origins and trust of consumers. The research indicates knowledge of how blockchain technology applies in various industries as a supply chain management. Also, the key challenges, preventions, and applications are discussed as and deeper understanding of modern supply chain management by improving the efficiency over technology.
Challenges in Traditional Supply Chain Management
One of the essential challenges in traditional supply management is the lack of transparency. There are many works in supply chain management, such as raw material supply, transport, and various deliveries, which include errors and accountability issues in the process (Subramany, 2024). There are security issues such as data breaches and hacking. And an observation of a financial loss in the process of product deliveries, and hacking the system. In traditional supply chain management, there are also delays and inefficiencies due to multiple transactions (Alrida, 2023). So, this led to a slowdown of the process and creation of errors. It requires more time and more movement of products, which leads to longer waiting times and lead times, and storage costs will be higher, which in turn affects the profitability.
There a complex network of manufacturers, retailers, and suppliers responsible for managing products so challenging for miscommunication and loss of items. There is also a lack of real-time visibility which in turn affects decision making and resource allocation, would be difficult. Inefficiency in inventory management where there are missed sale opportunities and is prone to errors. It had high lead times and slow response at the market change where it has an extension over timelines and delays of demand. There is a lack of traceability which damages brand reputation and compromise the safety of consumers. Resistance to technology adaptations where it continuously requires manual paperwork and promotion of data-driven solutions.
Blockchain’s role in enhancing transparency and security in Supply chain management
For improvement of transparency and security in the supply chain, the blockchain technology particularly creates a secure system for the stakeholders. In blockchain technology, real-time tracking provides faster deliveries when compared to traditional systems. In the traditional system, there was poor management of the tracking system. The blockchain enhances the decentralized Ledger, accessible for everyone for transactions and handling the goods. Moreover, this verifies the origins of purchase and also encourages demand for sourcing with transparency. It enhances security through immutable records, once the data is recorded in the blockchain, it is not removed. Security is managed and no hacking or human errors.
The information is not permanent. In the supply chain, product quality is important and it delivers supportive management. Another benefit is end-to-end traceability. In traditional systems, there is no visibility, but now every step in the journey of the product is transparent. Also, it is accessible for everyone, it provides quality and safety for all the goods and services. In pharmaceuticals, the tracking of drugs at every stage in the supply chain. The stakeholders verify the product is genuine and identify all the responsive management, and give quick responses. Moreover, there are disputes and it causes time delay in verifying the history. Each recorded transaction is accessible and the blockchain should have standards for maintaining the payments.
Blockchain in supply chain management
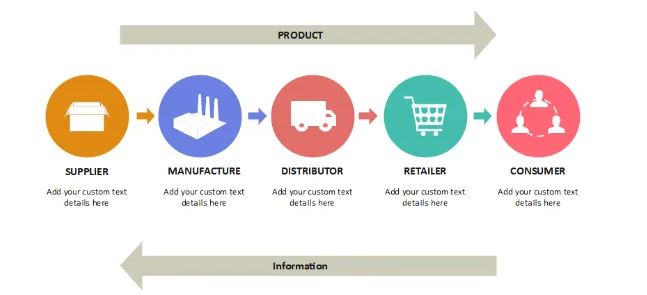
Real-world applications of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Case Study 1: Walmart food safety blockchain
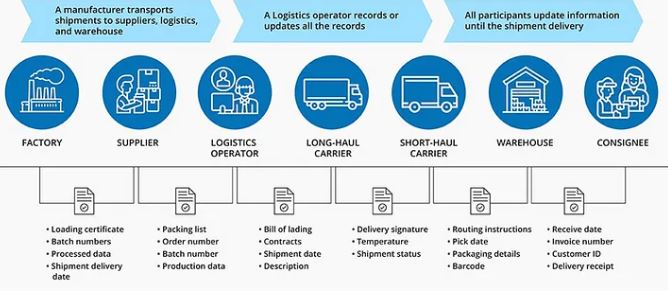
There is a partnership between IBM and Walmart about blockchain-based solutions for food tracking. It has a network with farmers manufacturers and various distributors. It has a record of the history of products and it maintains the automatic updates with the information. One of the advantages is that food products trace all the food products and minimize wastage. Moreover, It had transparency in maintaining the quality standards and reputation of the company. Also, It has encouraged good collaboration with IBM Food Trust and maintained supply chain management with effective and productive distributors and food safety measures (Kamath, 2018). Furthermore, Walmart with the involvement of the Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence for supply chain visibility and maintaining a more sustainable food supply.
Case Study 2: IBM Food Trust Network
IBM Food Trust network is also a great solution in food safety measures and management of manufacturers. One of the challenges is it has delays in hits product management and wastage management. The traditional tracking system had vulnerabilities and limitations over the supply chain. So, the blockchain solution gives transparent solutions and secured mechanisms for maintaining the products and good traceability to identify the contaminated products and it has promoted accountability in maintaining the suppliers and quality measures. It has efficiency in verification and automating processes.
Case Study 3: De Beers and Blockchain Technology for Diamonds
For instance, blockchain technology for tracking diamonds De Beers, is one of the great companies to combat fraud transactions and maintain its conflict-free resolutions. It has concerns over consumers and maintained solutions regarding platform management and quality management. Moreover, It has verified all the origins of diamonds and ethical practices. Also, It has ensured the genuine purchase of diamonds and proven the products are genuine and accountable. Furthermore, it has thought of eliminating unethical practices, and encourage trust in diamonds.
Process of blockchain in IBM and WALMART
Challenges and limitations of implementing blockchain in supply chain management
It is one of the major concerns in blockchain supply chain management. There are public blockchains such as Ethereum and Bitcoin which have large-scale transactions and a high volume of processing time. Blockchains depend on proof of work which leads to energy consumption and enhance the cost of transactions. These high-frequency transactions has scalability issues and need to slow down the transaction. Therefore, the proof of stake solutions should develop and need technologies for adoptions. There are integration issues that are not designed like blockchain and these need to be planned effectively.
Integrating blockchain with the existing infrastructures of software will be time-consuming, and also replacing it with them will result in synchronization issues and data consistency issues. The complexity in the management is higher, as financial investment is needed for better training and infrastructure. It involves a blockchain network with encryption and maintaining the standardized mechanism to train on the blockchain expertise. There are also regulatory and legal concerns regarding data privacy and complaints. The General Data Protection Regulation to modify the data and maintain sensitive customer data. Additionally, with the help of integration and the best legacy systems, and avoiding the scalability issue it enhances solutions and better management in the supply chain.
Conclusion
Blockchain management in real-time tracking of goods and visibility has become an important aspect of supply chain management it not only encourages accountability but also helps in the maintenance of all the goods and services by ensuring data integrity and security. The management of quality checks and operational management in SCM by providing and addressing inefficiencies in the blockchain. Furthermore, it has a promising experience with the introduction of AI protocols and the Internet of Things with high transactions and volumes of data maintenance. It is also helpful in maintaining the integration and management of industries. In summary, the blockchain is maintained with advancements and future implementations over the global issues and planning for enhancement of operations to reduce the inefficiencies.
References
Alrida, A. (2023, Feb 05). Challenges in Conventional Supply Chain Management. Retrieved from Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/challenges-conventional-supply-chain-management-ammar-alrida-
Hayes, A. (2024, Sep 16). Blockchain Facts: What Is It, How It Works, and How It Can Be Used. Retrieved from Investopedia: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/blockchain.asp
Kamath, R. (2018). Food Traceability on Blockchain: Walmart’s Pork and Mango Pilots with IBM. The Journal of British Blockchain Association, 1(1), 1-12. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326188675_Food_Traceability_on_Blockchain_Walmart’s_Pork_and_Mango_Pilots_with_IBM
Paul, P., Aithal, P., Saavedra, R., & Ghosh, S. (2021). Blockchain Technology and its Types—A Short Review. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 9(12), 189-200. Retrieved from https://ndpublisher.in/admin/issues/IJASEv9n2g.pdf
Subramany, R. (2024, AUG 20). The (Potential) Role of Blockchain in Enhancing Supply Chain Transparency and Security. Retrieved from Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/potential-role-blockchain-enhancing-supply-chain-randy-subramany-yzbve
Tripathi, G., Ahad, M. A., & Casalina, G. (2023). A comprehensive review of blockchain technology: Underlying principles and historical background with future challenges. Decision Analytics Journal, 9, 100-334. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772662223001844
Keywords
Cryptographic techniques, Blockchain, Supply chain management, Bitcoin, Transparency
Relevant Articles
Decentralized Identity Management: The Role of Blockchain
Blockchain for healthcare: Enhancing data security and patient privacy
Read More about the Topic
Blockchain Technology for Secure Supply Chain Management: A Comprehensive Review
